
“`html
Finance AES: Advanced Encryption Standard in Financial Security
In the increasingly digital landscape of finance, data security is paramount. Sensitive information, ranging from customer accounts and transaction details to proprietary trading algorithms, requires robust protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) has emerged as a cornerstone of financial security, providing a powerful and widely adopted method for safeguarding data confidentiality and integrity.
What is AES?
AES is a symmetric-key encryption algorithm, meaning the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. It operates on fixed-size blocks of data (128 bits) and supports key sizes of 128, 192, or 256 bits, denoted as AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256, respectively. Larger key sizes offer greater security but also require more computational resources.
Why AES for Finance?
Several factors contribute to AES’s widespread adoption in the financial sector:
- Strength: AES is considered highly secure, with no known practical attacks against it. Its robust design has withstood years of scrutiny by cryptographers, making it a trusted algorithm for protecting sensitive data.
- Performance: AES is relatively efficient, offering a good balance between security and performance. Modern hardware and software implementations can perform AES encryption and decryption at high speeds, minimizing the impact on transaction processing and other critical financial operations.
- Standardization: AES is a widely accepted standard, defined by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in the United States. This standardization ensures interoperability and compatibility across different systems and platforms, making it easier to integrate AES into existing financial infrastructures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many financial regulations, such as PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), mandate the use of strong encryption algorithms to protect sensitive data. AES often meets or exceeds these requirements, helping financial institutions comply with relevant regulations.
Applications in Finance
AES is employed in various financial applications, including:
- Data at Rest Encryption: Protecting stored data, such as customer databases, transaction logs, and financial records, by encrypting them at rest. This prevents unauthorized access in the event of a data breach.
- Data in Transit Encryption: Securing data transmitted over networks, such as online banking transactions, electronic fund transfers, and API communications, using protocols like TLS/SSL with AES encryption.
- Database Encryption: Encrypting entire databases or specific sensitive fields within databases to protect confidential information.
- Hardware Security Modules (HSMs): Using HSMs to generate, store, and manage AES keys securely. HSMs provide a tamper-resistant environment for cryptographic operations, reducing the risk of key compromise.
- Payment Systems: Protecting payment card data during processing and storage, ensuring compliance with PCI DSS requirements.
Considerations for Implementation
While AES is a powerful encryption algorithm, its effective use depends on proper implementation and key management practices. Key considerations include:
- Key Management: Securely generating, storing, distributing, and rotating AES keys. Key management practices are crucial to prevent key compromise.
- Mode of Operation: Choosing an appropriate mode of operation for AES, such as CBC (Cipher Block Chaining) or CTR (Counter), depending on the specific application requirements.
- Implementation Security: Ensuring the security of the implementation code to prevent vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits to identify and address potential weaknesses in the encryption system.
In conclusion, AES plays a vital role in securing financial data. Its strength, performance, standardization, and compliance benefits make it an essential tool for financial institutions seeking to protect sensitive information in an increasingly complex and threat-filled digital environment.
“`
 1400×1050 limportanza strategica del rendiconto finanziario yourcfo from www.yourcfo.it
1400×1050 limportanza strategica del rendiconto finanziario yourcfo from www.yourcfo.it
 1741×980 economy finance concept financial business investment statistics from www.vecteezy.com
1741×980 economy finance concept financial business investment statistics from www.vecteezy.com
 3920×1960 growth strategy business graph analysis concept finance chart data from www.vecteezy.com
3920×1960 growth strategy business graph analysis concept finance chart data from www.vecteezy.com
 1920×1280 guide venture capital financing roseryan from roseryan.com
1920×1280 guide venture capital financing roseryan from roseryan.com
 1920×1200 financial management concept investment flat design payment from www.vecteezy.com
1920×1200 financial management concept investment flat design payment from www.vecteezy.com
 4404×2906 personal finance corporate finance main difference from virtualggc.com
4404×2906 personal finance corporate finance main difference from virtualggc.com
 1920×1081 economy finance background financial business statistics from www.vecteezy.com
1920×1081 economy finance background financial business statistics from www.vecteezy.com
 1200×630 artificial intelligence impacting finance from www.chaserhq.com
1200×630 artificial intelligence impacting finance from www.chaserhq.com
 1600×1690 finance function business refers functions intended from www.dreamstime.com
1600×1690 finance function business refers functions intended from www.dreamstime.com
 1920×1080 embedded finance examples brimco from www.brimco.io
1920×1080 embedded finance examples brimco from www.brimco.io
 3640×2410 finance system icons symbols finance illustrations creative from creativemarket.com
3640×2410 finance system icons symbols finance illustrations creative from creativemarket.com
 1200×628 swine definition finance tracy macias blog from storage.googleapis.com
1200×628 swine definition finance tracy macias blog from storage.googleapis.com
 3888×2592 personal finance from www.love-and-i.com
3888×2592 personal finance from www.love-and-i.com
 1170×400 business finance continuing studies uvic from continuingstudies.uvic.ca
1170×400 business finance continuing studies uvic from continuingstudies.uvic.ca
 1920×1080 manage personal finance beginners guide from blog.shoonya.com
1920×1080 manage personal finance beginners guide from blog.shoonya.com
 961×574 embedded finance examples benefits opportunities from happay.com
961×574 embedded finance examples benefits opportunities from happay.com
 1920×1120 vector cartoon business finance management icon comic style from www.vecteezy.com
1920×1120 vector cartoon business finance management icon comic style from www.vecteezy.com
 2000×1250 finance wallpapers wallpaperdog from wallpaper.dog
2000×1250 finance wallpapers wallpaperdog from wallpaper.dog
 1600×840 personal finance software paid from shawnmanaher.com
1600×840 personal finance software paid from shawnmanaher.com
 2560×1969 top ai tools accounting marktechpost from www.marktechpost.com
2560×1969 top ai tools accounting marktechpost from www.marktechpost.com
 4000×3000 lhistoire de la finance histoire evolutions from www.wmag-finance.fr
4000×3000 lhistoire de la finance histoire evolutions from www.wmag-finance.fr
 1200×768 finance commission india functions article qualifications from www.studyiq.com
1200×768 finance commission india functions article qualifications from www.studyiq.com
 1024×975 finance animation explained keystone media from keystonemediahq.com
1024×975 finance animation explained keystone media from keystonemediahq.com
 1200×673 rendering glowing digital business interface showcasing finance from pngtree.com
1200×673 rendering glowing digital business interface showcasing finance from pngtree.com
 1200×628 finance bill kenya highlights from ronalds.co.ke
1200×628 finance bill kenya highlights from ronalds.co.ke
 1000×750 finance outsourcing comprehensive guide pros cons from www.hirewithnear.com
1000×750 finance outsourcing comprehensive guide pros cons from www.hirewithnear.com
 1920×1920 icone financeiro png from pt.vecteezy.com
1920×1920 icone financeiro png from pt.vecteezy.com
 720×720 accounting finance from www.linkedin.com
720×720 accounting finance from www.linkedin.com
 2560×1382 behavioral finance understanding biases tips overcoming from insights.masterworks.com
2560×1382 behavioral finance understanding biases tips overcoming from insights.masterworks.com
 4800×6592 applications generative ai financial services cb insights from www.cbinsights.com
4800×6592 applications generative ai financial services cb insights from www.cbinsights.com
 2400×1256 quick glance sources finance start from razorpay.com
2400×1256 quick glance sources finance start from razorpay.com
 1024×576 ways manage personal finances from hbr.org
1024×576 ways manage personal finances from hbr.org
 1766×986 finance definition studyslopecom from studyslope.com
1766×986 finance definition studyslopecom from studyslope.com
 2240×1260 guide structuring finance team cfo hub from cfohub.com
2240×1260 guide structuring finance team cfo hub from cfohub.com
 1600×1051 defi decentralized finance blockchain decentralized financial system from www.dreamstime.com
1600×1051 defi decentralized finance blockchain decentralized financial system from www.dreamstime.com
 1920×1920 set money finance icon logo vector illustration finance pack symbol from www.vecteezy.com
1920×1920 set money finance icon logo vector illustration finance pack symbol from www.vecteezy.com
 1500×1000 bangkok post unlocking power sustainable finance from www.bangkokpost.com
1500×1000 bangkok post unlocking power sustainable finance from www.bangkokpost.com
 1920×1440 cases chatgpt finance fusemachines insights from insights.fusemachines.com
1920×1440 cases chatgpt finance fusemachines insights from insights.fusemachines.com
 2160×1215 finance career from ar.inspiredpencil.com
2160×1215 finance career from ar.inspiredpencil.com
 1920×1152 finance images clip art from ar.inspiredpencil.com
1920×1152 finance images clip art from ar.inspiredpencil.com
 1720×918 top finance job titles ongig blog from blog.ongig.com
1720×918 top finance job titles ongig blog from blog.ongig.com
 1184×860 financial economics methods models faqs from www.vedantu.com
1184×860 financial economics methods models faqs from www.vedantu.com
 960×540 decentralized finance defi powerpoint template from www.collidu.com
960×540 decentralized finance defi powerpoint template from www.collidu.com
 1600×1600 financial logos from animalia-life.club
1600×1600 financial logos from animalia-life.club
 1024×576 structured finance work leia aqui from fabalabse.com
1024×576 structured finance work leia aqui from fabalabse.com
 960×540 public finance powerpoint template from www.collidu.com
960×540 public finance powerpoint template from www.collidu.com
 1000×563 finance software personal business from happay.com
1000×563 finance software personal business from happay.com
 2251×2251 supply chain finance work importance from www.dripcapital.com
2251×2251 supply chain finance work importance from www.dripcapital.com
 2000×2000 premium vector hand draw business finance doodle set vector from www.freepik.com
2000×2000 premium vector hand draw business finance doodle set vector from www.freepik.com
 2560×1645 healthcare finance management comprehensive guide from avonriverventures.com
2560×1645 healthcare finance management comprehensive guide from avonriverventures.com
 1000×833 modern financial logo design idea stock vector adobe stock from stock.adobe.com
1000×833 modern financial logo design idea stock vector adobe stock from stock.adobe.com
 1600×900 from www.pwc.tw
1600×900 from www.pwc.tw
 1201×1501 corporate financeth edition global edition softarchive from softarchive.is
1201×1501 corporate financeth edition global edition softarchive from softarchive.is
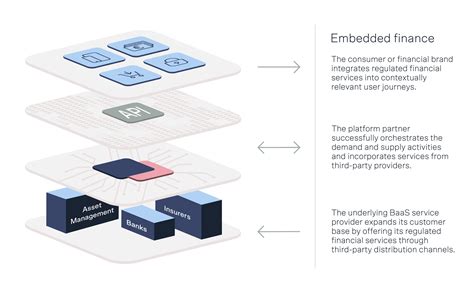 3700×2220 money management firms board embedded finance heres from www.solarisgroup.com
3700×2220 money management firms board embedded finance heres from www.solarisgroup.com
 1920×1080 personal finance important shoonya blog from blog.shoonya.com
1920×1080 personal finance important shoonya blog from blog.shoonya.com
 2048×2048 essentials corporate finance edition stephen ross randolph from www.prioritytextbook.com
2048×2048 essentials corporate finance edition stephen ross randolph from www.prioritytextbook.com